
Flasks Definition
Flasks are used to hold the sand mold in place during the casting process. A typical mold has 2 halves, the cope which is the top half, and the drag which is the bottom half. When a flask is applied to the outside of the mold, it holds the 2 halves together and prevents any shifting of the mold as it travels down the conveyor to be poured off at the furnace.
If the mold shifts in any way prior to being poured off, misaligning the 2 halves, the casting will also shift and have a mismatch at the parting line.
Types of Flasks in Sand Casting
Flasks are essential for stabilizing and supporting the mold during the casting process. The main types include:
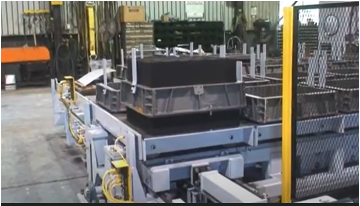

Cope and Drag Flask Sections
The cope (top) and drag (bottom) sections of the flask enclose the two halves of the mold, ensuring stability throughout each stage of casting. Both sections are precisely aligned to hold the mold securely, maintaining the accuracy of the pattern’s impression. During the mold-making process, alignment pins are often used to connect the cope and drag flasks, ensuring that no lateral shifting or misalignment occurs when the molten aluminum is poured, which helps prevent casting defects.
Preventing Mold Shift
Flasks are critical in preventing mold shift, a common casting defect that occurs when the two halves of the mold do not align perfectly. By tightly clamping the cope and drag together, the flask holds the entire mold assembly in place as it travels down the conveyor, ensuring dimensional accuracy and consistent quality. Flasks also provide structural integrity to the mold, enabling it to withstand the force and pressure of the molten aluminum during pouring and cooling without collapsing or misaligning.







